Passion fruit, scientifically classified as Passiflora edulis or Passiflora flavicarpa depending on its color, belongs to the Passifloraceae plant family. Among the 500 species within this plant family, passion fruit is renowned for its historically recognized medicinal properties.
This exotic fruit thrives in tropical and subtropical regions such as South America, South Africa, Florida, and the Caribbean. Its popularity continues to soar globally due to its purported health benefits.
With its distinctive purple or yellow hue, passion fruit boasts a tough outer rind encasing soft pulp filled with seeds. Both the seeds and pulp are edible, offering a plethora of essential nutrients including antioxidants, fiber, vitamins, and minerals that contribute to various aspects of health.
Abundant in Nutritional Value
Including passion fruit in a balanced diet can contribute to a strong immune system and lower the risk of illnesses due to its high nutrient content. It is especially rich in vitamin C, an antioxidant that enhances immune function, with a single small fruit providing nearly 10% of the recommended daily value.

Vitamin C, along with other antioxidants, combats oxidative stress and inflammation by neutralizing free radicals. It also aids in the production of white blood cells, the formation of tissue, and wound healing.
Additionally, passion fruit contains beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A. This vitamin is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and mucous membranes, which act as barriers against harmful pathogens.
Promotes Heart Health
Passion fruit is beneficial for heart health due to its high dietary fiber content, which helps regulate cholesterol levels. The soluble fiber, particularly pectin, in passion fruit binds to cholesterol in the digestive system, preventing its absorption and thereby lowering the levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or “bad” cholesterol in the body.

Additionally, a single passion fruit without the peel contains approximately 63 milligrams (mg) of potassium. Potassium is important for regulating blood pressure, which is crucial for maintaining heart health. However, it’s worth noting that one passion fruit provides only about 2% of the daily potassium requirement for an average healthy adult, who needs between 2,600-3,400 mg of potassium per day.
Improves Insulin Sensitivity
Passion fruit contains a phytochemical known as piceatannol, which has been associated with various potential health benefits in animal studies. Recent research involving human participants has indicated that supplemental piceatannol can enhance metabolic health markers in certain groups.
In one study, participants were given 20 mg of piceatannol daily, leading to improved insulin sensitivity in overweight men. This suggests that piceatannol, found in abundance in the seeds of passion fruit, may assist overweight men in utilizing blood glucose more efficiently.
Promotes Digestive Health
Passion fruit is rich in fiber, which provides numerous advantages for the gut microbiome. Ongoing research emphasizes the importance of gut health for overall well-being, indicating that an imbalance in the microbiome can trigger inflammation and contribute to chronic health issues. Foods that are high in nutrients and fiber support gut health by nourishing the beneficial bacteria in the digestive system.

Adults should aim for about 25-30 grams (g) of fiber each day, but many do not reach this goal. Consuming enough fiber is essential for regular bowel movements, maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, and managing blood sugar. A single passion fruit provides roughly 2 g of fiber while containing only 18 calories, making it a great option for increasing fiber intake without adding too many calories.
Promotes Healthy Skin
Passion fruit can also support skin health, as studies have suggested that piceatannol, a compound found in the fruit, has various beneficial effects on the skin. For instance, a recent study showed that using supplements containing passion fruit extract improved skin hydration and reduced signs of fatigue.

Additionally, passion fruit is rich in antioxidants such as vitamin C, which are vital for skin health. These antioxidants combat free radicals that lead to signs of aging and oxidative stress, a condition that can result in cell damage and disease. Furthermore, the vitamin A content in passion fruit aids in skin regeneration and helps maintain a clear complexion.
Nutritional Profile of Passion Fruit
Passion fruit is packed with nutrients, but due to its small size, it provides only modest amounts of vitamins and minerals, making it suitable for various therapeutic diets. In one passion fruit, none of the nutrients reach more than 10% of the recommended Daily Value.
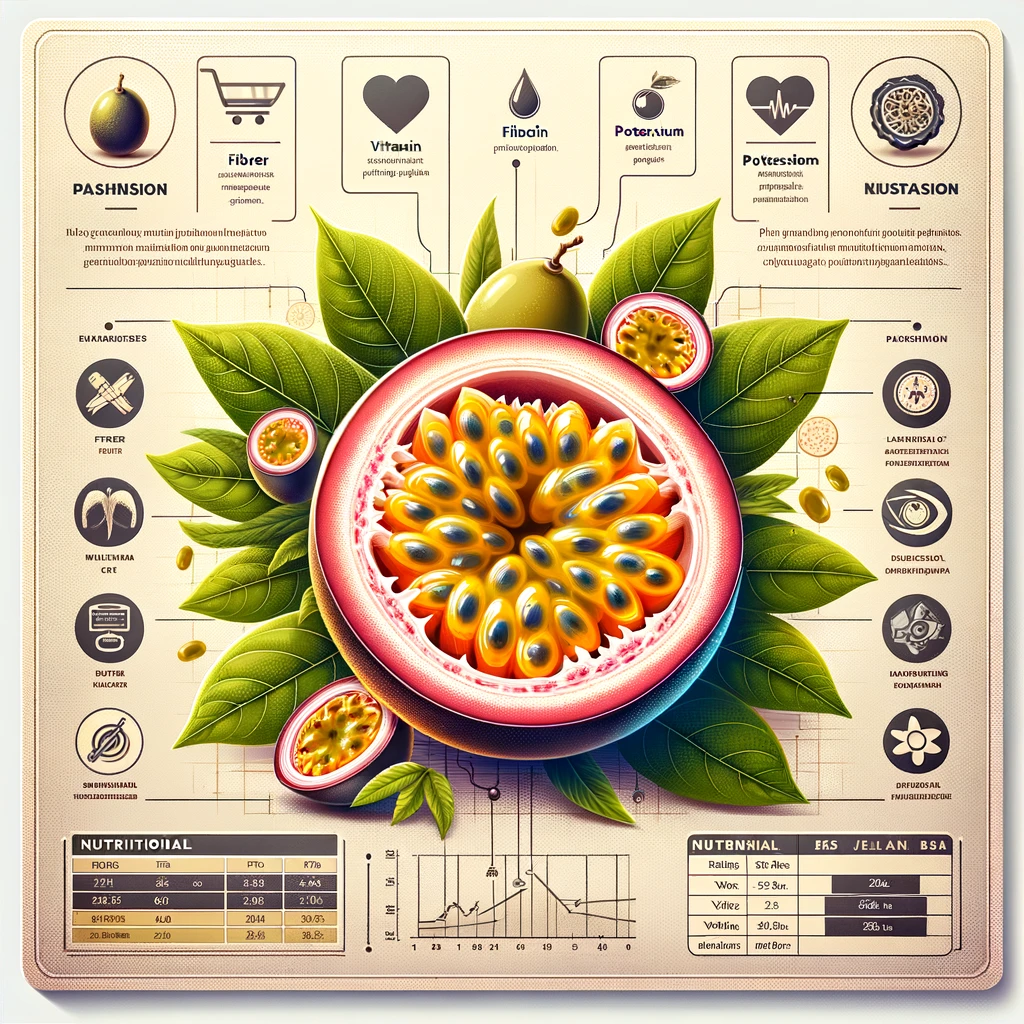
A single purple passion fruit provides the following nutrients:
- Calories: 17.5
- Protein: 0.4 grams (g)
- Carbohydrates: 4.2 g
- Fat: 0.12 g
- Fiber: 1.9 g
- Sodium: 5 milligrams (mg)
- Vitamin C: 5.4 mg
- Potassium: 62.6 mg
- Magnesium: 5.2 mg
- Vitamin A: 11.5 micrograms (mcg)
Although the nutritional content of passion fruit may appear modest in relation to recommended daily intakes, incorporating it into your diet can still contribute to a balanced nutritional regimen. Additionally, passion fruit is low in calories, making it an excellent choice for enhancing nutrient intake without significantly increasing your overall calorie consumption.
Potential Drawbacks of Passion Fruit
Passion fruit is generally safe for consumption. However, certain parts of the fruit, especially immature ones, contain cyanogenic compounds that can be toxic if ingested in large quantities. Symptoms of cyanide poisoning include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, and fatigue. The majority of these compounds are found in the peel, which is almost inedible, while the pulp and juice pose a lower risk.
If passion fruit is not suitable for your diet, there are other tropical fruits that offer similar nutritional benefits. Fruits like pineapple, mango, pomegranate, and peaches also have an acidic taste and provide comparable nutrients.
Guidelines for Enjoying Passion Fruit
Most individuals consume passion fruit in its raw form by cutting it in half and scooping out the flesh from the rind. The white membrane that divides the rind from the pulp is safe to eat, though it has a notably bitter flavor.
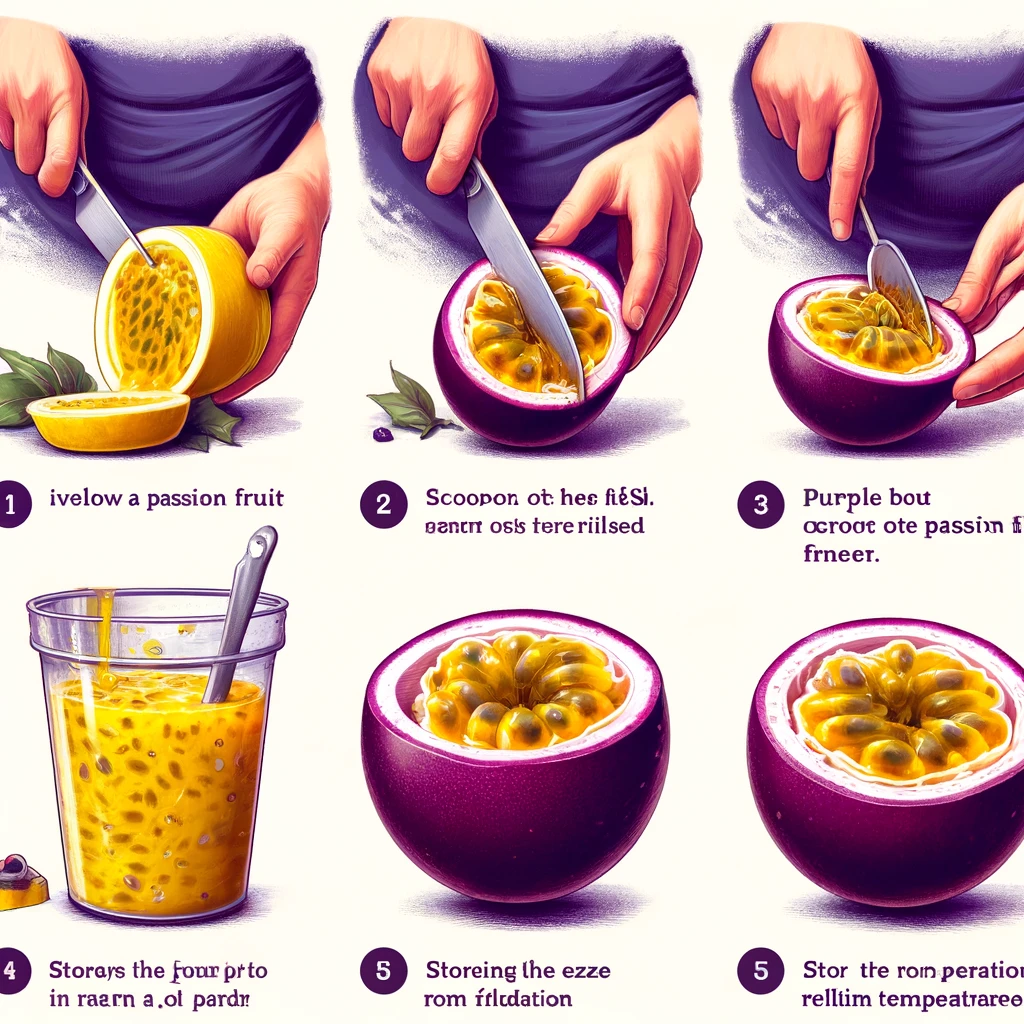
The yellow variety of passion fruit is generally bigger and more tart compared to the purple variety. Storing whole passion fruit at room temperature is fine, but refrigerating it can extend its shelf life.
Passion fruit can be enjoyed in several ways. Here are some ideas to consider:
- Press the passion fruit through a strainer and mix the juice into a variety of drinks and mocktails.
- Add passion fruit to yogurts and salads for a crunchy texture and a burst of sweetness.
- Use passion fruit as a topping for desserts to enhance their flavor.

